Action
Sub-Saharan Africa’s Difficult Road to Recovery
Published
5 years agoon
By ABEBE AEMRO SELASSIE, Director, African Department, IMF
The COVID-19 pandemic represents an unprecedented health and economic crisis for sub-Saharan Africa. Within months, the spread of the virus has jeopardized years of development and decades-long gains against poverty in the region while threatening the lives and livelihoods of millions of people.
In our latest Regional Economic Outlook, we project -3 percent growth in sub-Saharan Africa’s GDP in 2020, representing the worst outcome on record for the region. The drop will be even larger for economies dependent on tourism and commodity exports. Growth in the region should rebound modestly in 2021 to 3.1 percent, but for many countries, a return to 2019 levels won’t occur until 2022-24.
Countries in the region acted swiftly to protect their people from the worst of the crisis, but lockdown measures came with high economic and social costs. Policymakers in sub-Saharan Africa now face the added challenge of rekindling their economies with fewer resources and more difficult choices.
As the region looks toward the future, uncertainty over the path of the pandemic continues to loom over an enduring recovery.

Confronting policy constraints and hard choices
The top policy priority should be saving lives and protecting livelihoods through health spending and income and liquidity support for households and businesses. Even with limited funds, policymakers acted swiftly with what they had.
However, countries in the region entered the crisis with significantly less fiscal space than they had prior to the global financial crisis of 2008-09. COVID-19 related fiscal support in sub-Saharan Africa has averaged 3 percent of GDP—markedly less than what has been spent in other regions of the world.
Advanced economies have had the space to do “whatever it takes.” In sub-Saharan Africa no such luxury exists, as countries struggle to do “whatever is possible” with their scarce resources.
Limited resources will ultimately force difficult choices.
Fiscal policies needed to boost the economy will have to be balanced against debt sustainability—already a daunting challenge for many countries in the region. The need to support growth through monetary policy will need to be matched against maintaining external stability and longer-term credibility. Financial regulation and supervision measures are needed to address crisis-affected banks and firms but should not compromise longer-term growth.
All the while, efforts to stabilize and grow economies must be weighed against the need to maintain social stability while preparing for sustained and inclusive growth over the long term.

Calling on the global community for support
Without significant additional financial assistance, many sub-Saharan African countries will struggle to simply maintain macroeconomic stability while meeting the basic needs of their populations.
The IMF has taken swift action to cover a significant portion of the region’s needs by providing about $16 billion financing this year alone to 33 countries and immediate debt service relief to 22 of the poorest, most vulnerable sub-Saharan African countries. We are working with countries to put in place governance mechanisms to help ensure that the funds benefit their people as intended.
We have also worked with the G20 to suspend debt service payments to official bilateral creditors and welcome the extension of the Debt Service Suspension Initiative.
But more help is needed. Sub-Saharan Africa faces additional financing needs of $890 billion through 2023. Private financial flows are expected to fill less than half of that need, while current commitments from international financial institutions and bilateral donors will cover only one-quarter of the need. Under that scenario, the region still faces a projected financing gap of $290 billion through 2023.
No country should have to choose between paying their debt or providing food and medicine for their people. To prevent the loss of decades-worth of development gains, the region will need access to more grants, concessional credit, and debt relief.
Looking toward a brighter future
Despite an uncertain outlook, the potential of sub-Saharan Africa and the resourcefulness of its people remain clear. Now is the time for lasting transformational reforms.
Sub-Saharan Africa will find its way back to a path of green, sustainable and inclusive development. The pandemic has presented a historic opportunity to build a better future and the international community has an important role to play.
Fostering better transparency and governance to improve trust in rule of law, strengthen business conditions and encourage external support will be a key element for developing a better future. Transformative domestic reforms to improve revenue mobilization, digitalization, trade integration, competition, social safety nets, and climate-change mitigation will be critical for the region’s resilience, growth and job creation.
Nelson Mandela once said, “may your choices reflect your hopes, not your fears.” The long climb out of this crisis won’t come easy, but the actions and choices of today will be vital for a prosperous and resilient future for sub-Saharan Africa.
Culled from IMF Blog
You may like
-


OmniRetail Emerges First in Financial Times’ Ranking of Africa’s Fastest-Growing Companies
-

M-KOPA raises $250m to scale high-impact consumer fintech across Africa
-


African FinTechs Set to Supercharge Business Growth and Employment
-


Satellite Technology Key to Saving Life As Natural Disasters May Rise 37% By 2025
Action
MTN Foundation Launches Skills Academy to Train 3 Million Nigerians
Published
10 months agoon
April 27, 2025The MTN Foundation has officially launched its Skills Academy, a transformative digital learning platform designed to empower millions of Nigerians with access to digital and financial skills essential for the 21st-century economy. The launch event, held at the Transcorp Hilton in Abuja, brought together top government officials, education stakeholders, and technology experts, reinforcing the importance of public-private collaboration in building a digitally inclusive Nigeria.
The platform, available at skillsacademy.mtn.com, is open to individuals aged 13 and above, whether in school, recently graduated, self-employed, or unemployed. It also features a career guidance tool to help secondary school students and other users explore pathways aligned with their strengths and market demand.
With youth unemployment over 6% and more than 18.3 million children out of school, according to the latest data from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), Nigeria faces a pressing need to close the digital skills gap. The Skills Academy directly responds to this challenge by offering free, self-paced courses and certifications in high-demand areas such as data analysis, software engineering, digital marketing, and project management.
In her welcome address, Dr. Mosun Belo-Olusoga, Chairman of the MTN Foundation (represented by Simon Aranonu, Director of the MTN Foundation), stated, “We believe digital skills are a truly powerful asset. No Nigerian youth or child should be left behind because of their socioeconomic background. This platform is designed to provide world-class learning experiences, helping Nigerian youth thrive and become future leaders.” To date, the platform has over 7,000 people learning and over 3,000 courses completed, setting a strong foundation for nationwide scalability.
The Honourable Minister of Communications, Innovation and Digital Economy, Dr. Bosun Tijani, in his keynote, described the platform as “unique and critical.” “Nigeria is a country that is extremely blessed. With an average age of just 16.9, we are one of the youngest populations in the world. This program is not just about training; it’s about equipping a generation that will drive innovation, deepen our economy, and position Nigeria as a net exporter of tech talent,” the Minister commented.
Odunayo Sanya, Executive Director of the MTN Foundation, added, “We are focused on building Africa’s largest digital talent pipeline. Through relevant and practical courses across various disciplines, offered in collaboration with the global e-learning platform Coursera, this web-based training system will be instrumental in promoting a digitally skilled workforce.”
This initiative is part of the MTN Foundation’s broader Digital Skills for Digital Jobs programme, which aligns with the Nigerian Government’s National Digital Economy Policy and Strategy (NDEPS) and Sustainable Development Goal 4: Quality Education.
Action
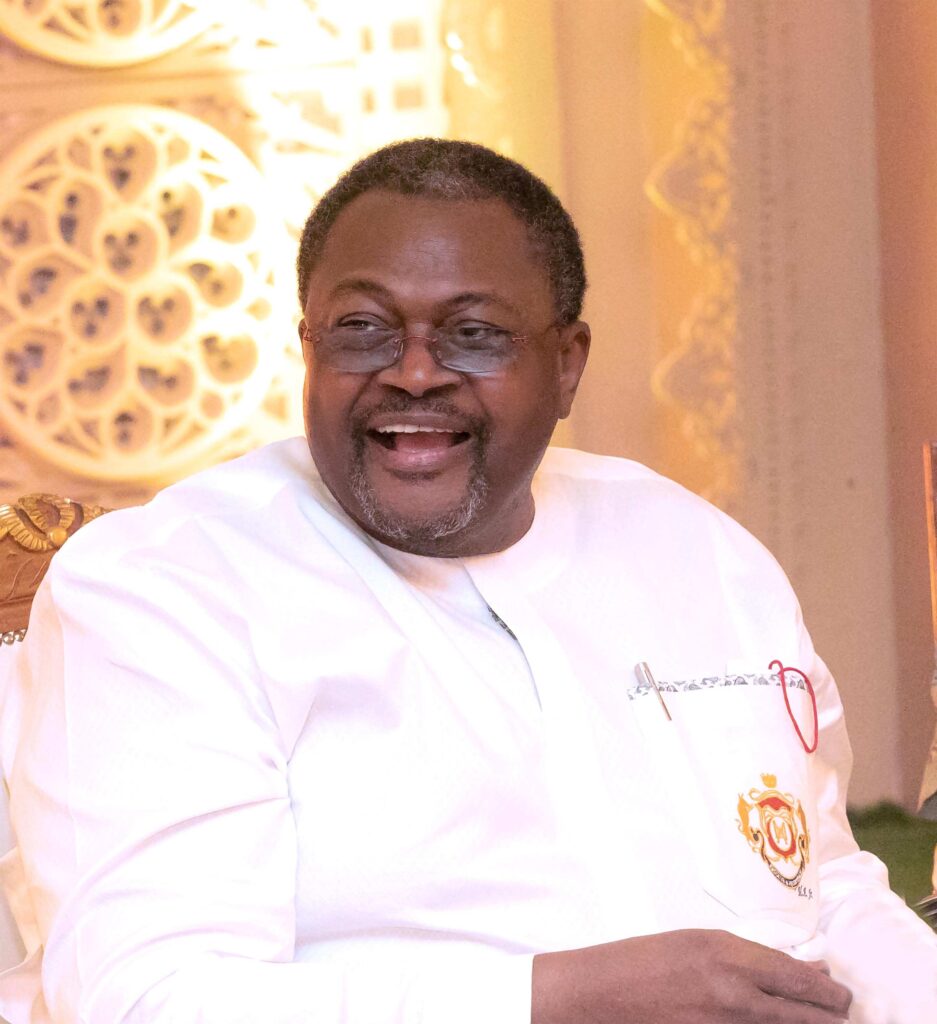
Mike Adenuga@72: The Man Who Democratized Mobile Telephony in Nigeria
Published
10 months agoon
April 27, 2025The Guru. Visionary. Pacesetter. Colossus. Transformer.
Happy birthday to Otunba Dr. Mike Adenuga (Jnr.), Chairman of Globacom and Conoil PLC as he marks his 72 years birthday on Tuesday April 29, 2025. Cheers to one Nigerian who bestrides the African business landscape.
A special gift to Nigeria, he is renowned for his business acumen. When it is comes to business, he’s got the vision. He can see good fortune light years ahead while others are still pandering whether it is feasible.

Dr. Mike Adenuga (Jnr.) is unafraid to venture where others fear to tread. Fondly called ‘The Bull’ for his fearless and zeal. He’s got this Midas touch that is unparalleled. His boundless energy, philanthropy, native intelligence and wisdom combined stand him out, enabling him to see ahead of others the right sectors and businesses to invest and transform.
Changing Telecom Services Narrative
If there is anyone who single-handedly transformed Nigerian telecommunications industry, that person is no other than Dr. Mike Adenuga (Jnr.). His tenacity to recover his Digital Mobile Licence (DML) which his company won in 2001 mobile auction but was illegally taken away from him, paid off in 2002 when his company, Globacom won the Second National Operator (SNO) licence.
In September 2003, Globacom transformed the Nigerian telecoms market in particular and Africa in general by being the first Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) operator to launch operations with Per Second Billing, Multimedia Service (MMS), Mobile Internet, in additional to plethora of communications suites simultaneously.
Glo crashed the price of Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) card, leaving other foreign mobile networks scratching their heads in the GSM wars that changed the face of telecom, bringing down the price of SIM Card from N50,000 down to N100 and later to One Naira (N1) only.
Millions of Nigerians became overnight owners of mobile phones lines courtesy of the competition engendered by Glo. Every major step Glo took from the day it commenced operation, other mobile competitors were jittery, helpless and followed the initiative in other to remain in the market.
After establishing the footprints of Glo in Nigeria, Dr. Mike Adenuga (Jnr.), also took the telecom giant to Ghana and Benin Republic with mobile operating licences in those countries. Unsatisfied with the routing of calls from Africa countries to Europe then back to Africa, he built Glo-1, the first international submarine cable system that was solely financed by an individual. Today, Glo-1 links global telecom networks, data centres, banks and Interconnect houses to millions of businesses across the world.
Globacom has going a notch higher with Glo-2 ensuring that Nigerian cities, towns and villages and oil companies are connected to terrestrial fibres through its landing stations in Lagos and Niger Delta.

Digital Financial Services
Dr Adenuga (Jnr.), a man who can see opportunities from afar, has took the lead in procuring Super-Agent licence for Agency Banking and Mobile Money licence from the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) with the establishment of Glo Mobile Money and Money Master Payment Service Bank Limited, a Digital Bank delivering financial inclusion services to Nigerians especially in rural, semi-rural and urban areas thus connecting them to the formal sector.
Oil, Gas Transformations
He transformed the face of Nigerian oil, banking, and telecommunications industries. In 1991, when oil mining and production was controlled by foreign multinational companies (MNCs), Dr. Adenuga’s (Jnr.) indigenous oil company was the first to start drilling crude oil. Today, Conoil has metamorphosed into one of the largest African-owned oil conglomerates on the continent with footprints in the upstream, midstream and downstream of the oil and gas sector.
His forays into the bank industry are well documented where he brought a fresh energy and bespoke financial services with Devcom Merchant Bank and Equatorial Trust Bank (ETB) which later merged into Sterling Bank.
Man flowing with Milk of Human Kindness
The humanitarian side of this famous Nigerian billionaire is incomparable. Although, coming from a middle-class family, Dr. Mike Adenuga’s (Jnr.) academic sojourn in the United States of America and the everyday life lessons internalized from his parents, Chief Michael Agbolade Adenuga (Snr) and Madam Oyindamola Adenuga, shaped his worldview and brought out his humane side in the way he deals with people and businesses.
He has been a major supporter of sports, especially football (Nigerian national teams). He has massively sponsored the Confederation of African Football (CAF) Awards for many years. He was honoured the title of Pillar of Football in Africa for his strong support for African Football at both national and continental. He has quietly rendered support to many without seeking media attention.
Through him, Glo sponsors the annual Ojude Oba festival in Ijebuland and also the Ofala festival in Onitsha, Anambra amongst others, promoting Nigeria’s rich culture. He has been major supporting of the Nigerian entertainment industry, turning many Nigerian and Ghanaian actors into instant millionaires through the Glo Ambassador programme.
A lover of education and the arts, Dr. Mike Adenuga (Jnr.) through his companies has sponsored several initiatives such as Glo Campus, and offered scholarships to thousands of the downtrodden to pursue their academic dreams.
Humble Beginnings
A man of outstanding wisdom, Dr. Mike Adenuga (Jnr.) was born Michael Adeniyi Agbolade Ishola Adenuga on April 29, 1953 at Ibadan, Oyo State. His father was a school teacher while his mother was an outstanding businesswoman.
Dr. Adenuga (Jnr) is an alumnus of the famous Ibadan Grammar School, North Western State University, Alva Oklahoma; and Pace University, New York, both in the United States of America where he majored in business administration with emphasis in marketing. As a student in the USA, he supported himself with jobs as a taxi driver and security guard.
Dr. Mike Adenuga (Jnr) is a visionary leader, an outstanding entrepreneur and and manager of people and resources. He is a man of uncommon intellect and wisdom have helped him overcome difficult times. Today, he sits atop a vast telecom, oil and gas (Conoil), banking and real estate investments.
As Dr. Mike Adenuga (Jnr) clocks 72 years on Tuesday April 29th, 2025, SiliconNigeria.ng wishes him a marvelous birthday and many happy returns in good health in the service of the fatherland.
Action
Africa’s Tech Skills Development Goes Beyond the Classroom-SAP
Published
2 years agoon
June 13, 2024Tech skills development in Africa is increasingly going beyond the borders of the classroom as organisations take novel approaches to addressing pervasive skills availability constraints.
Kholiwe Makhohliso, Managing Director at SAP Southern Africa, says upskilling and mobilising Africa’s considerable skills base is a defining opportunity for the future success of the continent. “Digital technologies continue to shape industries and businesses throughout the continent, driving high levels of demand for professionals with relevant skills. As the pace of technological change continues to accelerate, organisations increasingly need new approaches to skills development to keep in step with the latest advances in cloud, AI and other transformative technologies.”
SAP’s 2023 report ‘Africa’s Tech Skills Scarcity Revealed’ laid bare significant challenges with skills availability among organisations in South Africa, Kenya and Nigeria. The report revealed that low levels of tech skills availability affect most organisations, with four in five companies reporting negative consequences from a lack of tech skills.
While the tech skills gap persists globally – with McKinsey finding that 87% of global senior executives reported their companies were not adequately prepared to address the skills gap – the situation can be more acute for African organisations.
Cloud, AI skills in high demand
According to Manos Raptopoulos, President: SAP EMEA, skills availability has become even more important in light of the ongoing impact of cloud and artificial intelligence on the region. “Enterprises throughout the region are leveraging powerful new cloud and AI capabilities to transform their business models and accelerate growth and innovation. As the business landscape becomes increasingly shaped by the power of these technologies, organisations need access to relevant skills to ensure they reap the benefits of the cloud and AI revolution.”
SAP launched new learning opportunities for developers in 2023, focusing on cloud and generative AI capabilities. SAP Build Code solutions offer AI-powered productivity tools for developers and draws on the power of SAP’s AI co-pilot Joule to boost productivity and embed code generation capabilities for a range of applications, from data model and application logic to test script creation.
The company also launched new role-based certification and free learning resources for back-end developers in 2023 as part of a global commitment to upskill two million professionals by 2025.
Work-ready skills for graduates
The SAP Young Professionals Program (YPP), offered by the Digital Skills Centre of SAP, extends the company’s skills development efforts to graduates. YPP is aimed at enabling young talent to utilise the latest SAP technology and innovation, and covers software functional and technical knowledge and certification, with a strong focus on the latest technologies and a range of soft skills to ease entry into the workplace.
Since its launch in 2012, the SAP Young Professionals Program has trained and graduates more than 4100 candidates across 41 countries, including over 1900 in Africa alone.
Vincent Mabeka, a 2023 graduate from South Africa, says the SAP Young Professionals Program helped him improve his skills, learn about new technologies and gain hands-on experience and unlock new job opportunities.
“The Young Professionals Program required dedication, hard work and passion, but rewarded me with guidance, feedback and recognition for my skills and capabilities. This has helped me secure a job as an SAP Solutions Advisor where I apply the knowledge and skills I learned to exciting projects. Thanks to the resources and network I developed during my time on the program, I continue to learn and expand my skills and abilities.”
Youth skills development in focus
With the world’s fastest-growing youth population, any digital skills efforts in Africa must extend to the continent’s young people. Africa’s working-age population is predicted to grow to more than 600 million by 2030, constituting a quarter of the world’s under-25s. But digital skills remain elusive among Africa’s youth, despite a projected 70% of jobs expected to require digital skills by the end of the decade.
Enter SAP Africa Code Week (ACW), a coding skills development programme aimed at youth that is held annually in partnership with UNESCO, the Association for the Development of Education in Africa, and Irish Aid.
Since its inception in 2015, ACW has successfully empowered 17 million young people across 54 countries with coding and computational thinking skills, while close partnerships with NGOs and governments across the continent has helped drive the inclusion of coding in national curricula.
Toward the end of 2023, SAP also announced a new pilot project in partnership with UNICEF and other public-private organisations aimed at preparing underserved youth for the digital workforce. The SAP Educate to Employ initiative targets youth aged 16 to 24 and provides soft skills foundational knowledge using the Student Zone portal on SAP’s learning site. The knowledge prepares youth for a possible career in technology, with potential roles in development, consulting and support.
Makhohliso says the support of a broad range of partners is essential to overcoming youth skills challenges on the continent. “By directly addressing youth unemployment and inspiring our vibrant youth to pursue careers in the exciting world of technology, we together with our partners hope to mobilise the potential of our continent to become leading players in the future digital economy.”